计算机各层次执行速度
条评论计算机系统的内部设计、各类应用架构无不是受此影响。
比如:为了平衡CPU速度不断提升,但是内存频率没有同步提升带来的协同问题,CPU从没有片内缓存到L1、L2、L3相继出现。又比如,网络多IO请求磁盘速度无法满足要求,催生了redis缓存。
计算机存储体系
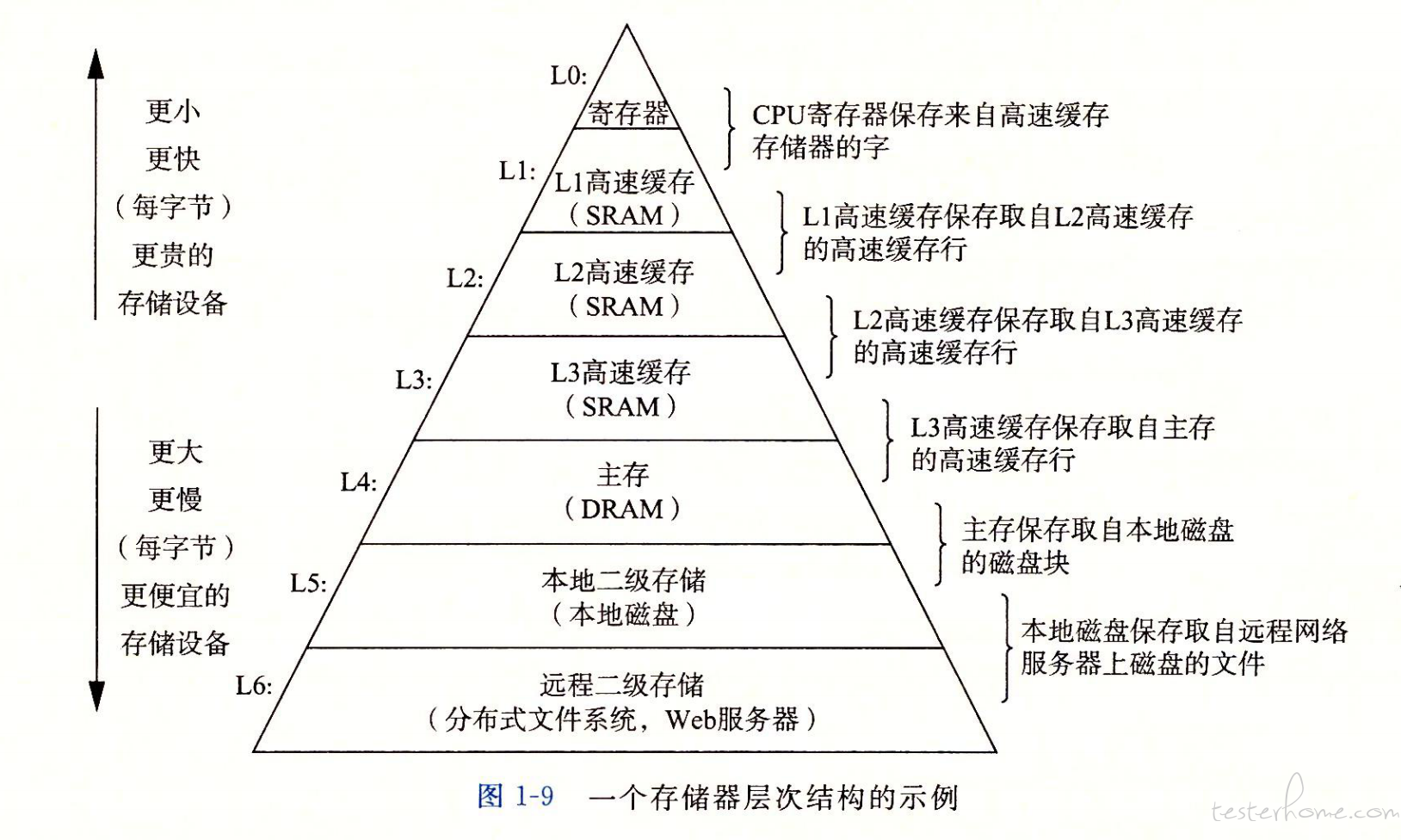
图:《深入理解计算机系统》
时间和空间局部性原理 决定了上一层级做下一层级的缓存;
计算机各层次速度表
| 序号 | 存储英文名称 | 存储中文名称 | 容量 | 时间(纳秒) | 微秒 | 毫秒 | CPU时钟周期数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CPU寄存器 | 几十~几百KB | 0.5 | 1 | |||
| 2 | L1 cache reference | 读取CPU一级缓存 | 几十~几百KB | 0.5 | 1 | ||
| 3 | Branch mispredict | (转移、分支预测) 比如:if | 5 | 10 | |||
| 4 | L2 cache reference | 读取CPU的二级缓存 | 几百KB~几MB | 7 | 14 | ||
| 5 | Mutex lock/unlock | 互斥锁\解锁 | 25 | 50 | |||
| 6 | Main memory reference | 内存引用(找到内存地址) | 几百MB~几GB | 100 | 0.1 | 200 | |
| 7 | Compress 1K bytes with Zippy | 使用Zippy压缩1K字节数据 | 3000 | 3 | 6000 | ||
| 8 | Send 1K bytes over 1 Gbps network | 在1Gbps的网络上发送1k字节 | 10,000 | 10 | 0.01 | 40000 | |
| 9 | Read 4K randomly from SSD | SSD磁盘随机读4k | 150,000 | 150 | 0.15 | 300,000 | |
| 10 | Read 1 MB sequentially from memory | 从内存顺序读取1MB | 250,000 | 250 | 0.25 | 500000 | |
| 11 | Round trip within same datacenter | 从一个数据中心往返一次,ping一下 | 500,000 | 500 | 0.5 | 1000,000 | |
| 12 | Disk seek | 磁盘搜索 | 几百GB~几TB | 10,000,000 | 10,000 | 1 | 20,000,000 |
| 13 | Read 1 MB sequentially from network | 从网络上顺序读取1兆的数据 | 10,000,000 | 10,000 | 1 | 20,000,000 | |
| 14 | Read 1 MB sequentially from SSD | 从SSD磁盘顺序读出1MB | 30,000,000 | 30,000 | 3 | 60,000,000 | |
| 15 | Send packet CA->Netherlands->CA | 一个包的一次远程访问 | 150,000,000 | 150,000 | 15 | 300,000,000 |
表引自(有修改):https://gist.github.com/jboner/2841832
寄存器速度等于CPU时钟周期,表假设CPU的1次晶振频率0.5纳秒,对应CPU2.0GHz。
原表格:
| Name | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L1 cache reference | 0.5 | ns | |||||
| Branch mispredict | 5 | ns | |||||
| L2 cachereference | 7 | ns | 14x L1 cache | ||||
| Mutex lock/unlock | 25 | ns | |||||
| Main memory reference | 100 | ns | 20x L2 cache, 200x L1 cache | ||||
| Compress 1K bytes with Zippy | 3,000 | ns | 3 | us | |||
| Send 1K bytes over 1 Gb ps network | 10,000 | ns | 10 | us | |||
| Read 4K randomly from SSD | 150,000 | ns | 150 | us | ~1GB/sec SSD | ||
| Read 1 MB sequentially from memory | 250,000 | ns | 250 | us | |||
| Round trip within same datacenter | 500,000 | ns | 500 | us | |||
| Read 1 MB sequentially from SSD | 1,000,000 | ns | 1,000 | us | 1 | ms | ~1GB/sec SSD, 4X memory |
| Disk seek | 10,000,000 | ns | 10,000 | us | 10 | ms | 20x datacenter roundtrip |
| Read 1 MB sequentially | 20,000,000 | ns | 20,000 | us | 20 | ms | 80x memory, 20X SSD |
| Send pack et CA->Netherlands->CA | 150,000,000 | ns | 150,000 | us | 150 | ms |
注:本文首次发表在testerhome,搬移过来。